Windows 8, the next generation OS from Microsoft comes with many notable changes which includes the new start screen, Windows Explorer and also the new task manager. Another new feature added to Windows 8 is the Storage Spaces. Storage spaces feature allows you to add physical disks into what is called as a storage pools and then creating virtual disks using these pools. You can also use the two way mirror feature of Storage space, which means data is stored in at least two disk which protects it from any disk failures.
Two main features of Storage Spaces include:
- Organization of physical disks into storage pools, which can be easily expanded by simply adding disks. These disks can be connected either through USB, SATA (Serial ATA), or SAS (Serial Attached SCSI). A storage pool can be composed of heterogeneous physical disks – different sized physical disks accessible via different storage interconnects.
- Usage of virtual disks (also known as spaces), which behave just like physical disks for all purposes. However, spaces also have powerful new capabilities associated with them such as thin provisioning (more about that later), as well as resiliency to failures of underlying physical media.
Storage spaces can be created from Control Panel (starting from Windows 8 Beta builds).
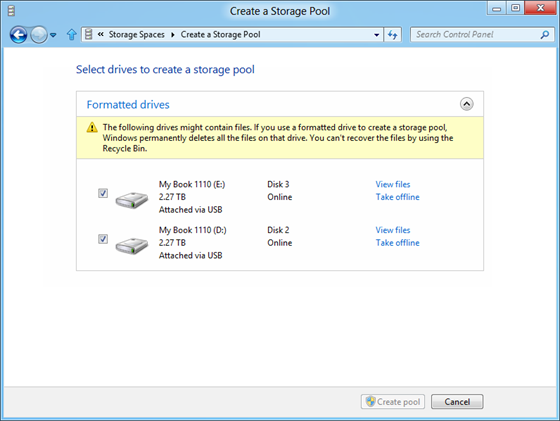
You can select the drives to create a storage pool, these can be connected to PC using a USB as well.
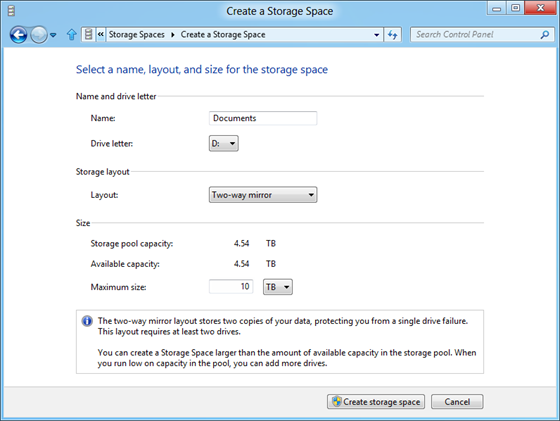
Once the storage pool is ready, you can create the spaces from these pools. The two way mirror layout makes sure that data is stored in at least two disks.
Note that once physical disks have been added to a pool, they are no longer directly usable by the rest of Windows – they have been virtualized, that is, dedicated to the pool in their entirety. For using the two way mirror feature, you need to have a minimum of two drives attached to the storage pool. The concept of Storage space is interesting especially from the data protection point of view.
To understand more on this feature, check the Windows 8 blog post with FAQs.