Hibernation in Windows is the process of saving memory and device context on the disk. Hibernation helps extend usable battery life on mobile PCs by saving the user’s open programs and documents on the disk and powering off the computer. Windows supports hibernation by copying the contents of memory to disk. The system compresses memory contents before preserving them on the disk, which reduces the required disk space to less than the total amount of physical memory on the system.
Hiberfil.sys file is used to set the reserve disk space for hibernate option in Windows. For Windows, the default size of the hibernation file is 75 percent of the total physical memory on the system. For example, if your PC has a 2 GB of RAM, the default hibernation file size is 1.5 GB. If you feel that the size of hibernation file is less than or more than required, you can always change the default file size set for hibernation.
To change the hibernation file size follow the steps below;
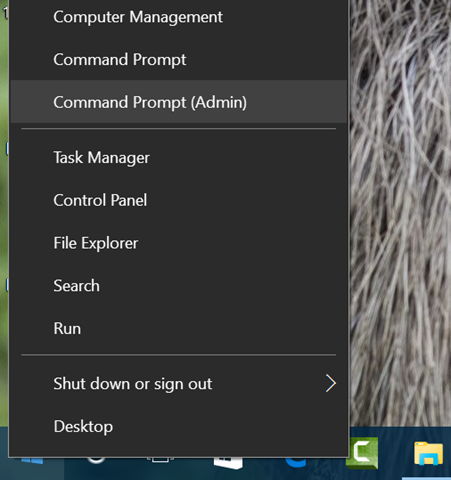
1. Open the Command prompt in Administrator mode. To do this, right click on the start menu in Windows 10 and select the option Command prompt (admin) from the list.
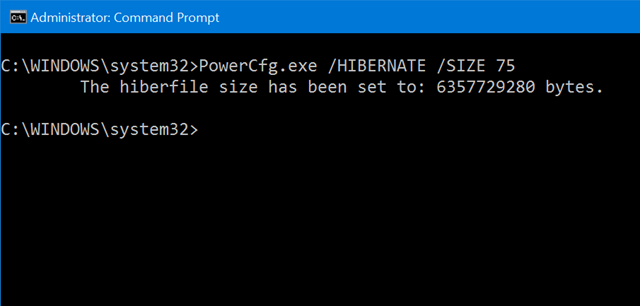
2. PowerCfg utility is used to change the hibernation file size in Window and we will use this utility to change the file size. In the command prompt, type PowerCfg.exe /HIBERNATE /SIZE percentage, where HIBERNATE and SIZE are PowerCfg parameters and you need to specify the percentage. For example if you want to set the file size as 75%, use the command PowerCfg.exe /HIBERNATE /SIZE 75.
When you press enter, you can see that the new file size for hibernation file will be 75% of what it used to be. Similarly, you can enter any percentage you want.
3. If you are not using the hibernation feature, you can also turn it off. To disable hibernate for the system, use the /HIBERNATE parameter with the “off” value: PowerCfg.exe /HIBERNATE off. This will turn off hibernation completely.