Data Execution Prevention (DEP) is a system-level memory protection feature that is built into the Windows OS starting with Windows XP and also available in Windows 10. The protection feature help prevent damage to your computer from viruses and other security threats. DEP can help protect your computer by monitoring programs to make sure they use system memory safely.
In case of any app or service executes codes from the memory in an inappropriate way, DEP closes the program and protects the PC.
If an application attempts to run code from a protected page, the application receives an exception with the status code. You can either enable DEP for all processes or specifically turn off DEP for particular program. To do this, open File Manager or Explorer in Windows 10 and right click on This PC and select properties.
From the System Properties window, select ‘Advanced system properties’ link available on the left side. Now select the advanced tab and choose the ‘Performance’ section. Finally select the Data Execution prevention tab from the performance window.
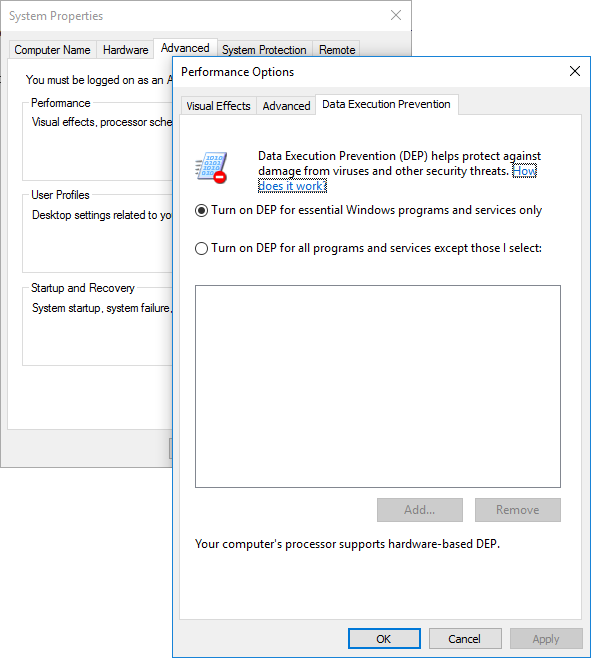
Here you get two options:
- Turn on DEP for essential Windows programs and services only
- Turn on DEP for all programs and services except those I select.
If you are selecting the second option, you can add the list of programs and services which you do not want to include in DEP.