For any PC, the RAM is one of the most important aspects and if there are any issues or failures in the functioning of RAM, then it will cause issues with the PC. So you need to keep a check on the performance of RAM on your PC. But quite often when a PC is showing signs of issues like lagging or not performing, then it could also be due to issues in RAM. So how do you detect RAM failures in Windows?
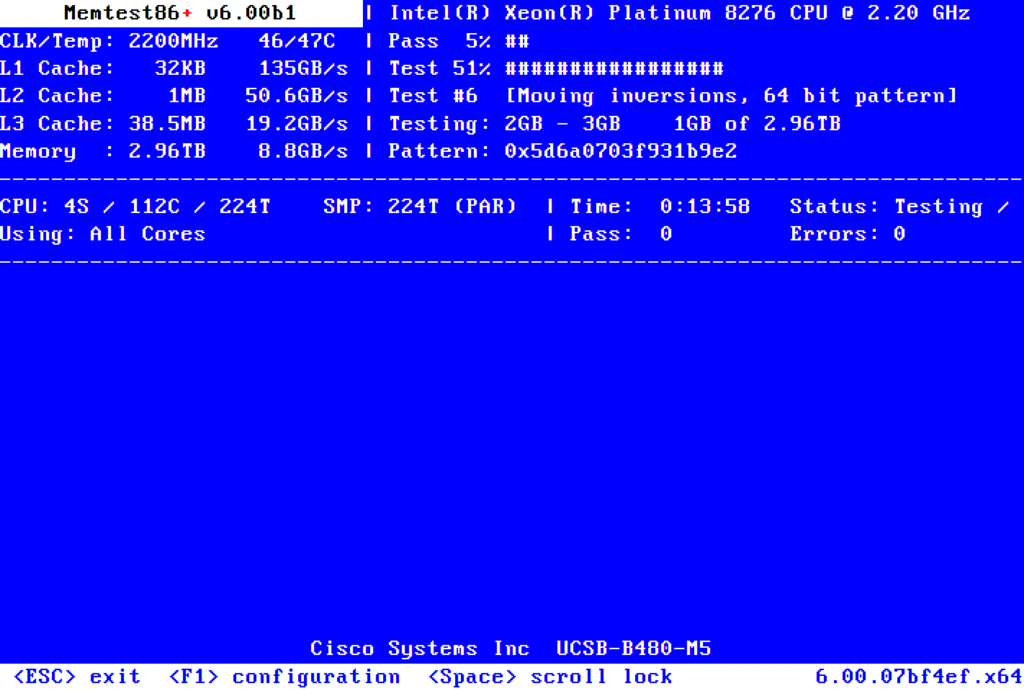
Memtest86+ is a stand-alone free application that is a memory tester for x86 and x86-64 architecture PCs and it helps you detect RAM failures. It provides a thorough memory check than that provided by BIOS memory tests. Memtest86+ can be loaded and run either directly by a PC BIOS (legacy or UEFI) or via an intermediate bootloader that supports the Linux 16-bit, 32-bit, 64-bit, or EFI handover boot protocol. It should work on any Pentium class or later 32-bit or 64-bit x86 CPUs as well.
This tool works outside of the operating system, which means you will need to create a bootable disk for checking the performance of your RAM. The app’s interface allows you to create a bootable disk and makes it easy to deploy it. Once you boot the PC next time to this disk, the app will perform the stress test on your PC. The app offers a few tests: you can choose how much of your RAM to test, and it also checks the CPU testing part. As RAM is interrelated with the processor, both components will be simultaneously tested with the app.
The app will do the test multiple times and if you want a quick result, you can stop it after a few rounds. But the longer the test runs, the more accurate the results will be. Memtest86+ is an endless loop. After a successful pass, all your memory has been tested successfully. You can wait for more for even greater confidence, or just remove your USB Drive and press ESC to stop. The app is a pretty useful tool to figure out issues and failures with RAM and processors. It is available as a free tool.
The Memtest86+ binary is actually not signed by Microsoft, so you need to temporarily disable Secure Boot in your BIOS options.